
Climate change and agriculture
At a time when our planet is witnessing increasingly evident climatic changes, the agricultural sector is one of the most affected by these unprecedented transformations. Indeed, by its very nature, agriculture is an activity that is immediately affected by climatic anomalies and sudden changes in environmental variables. Have you ever thought about how your breakfast would change if coffee or wheat suddenly became hard to come by?
Climate change has led to an increase in the frequency and intensity of weather events, putting a strain on the resilience of crops and agricultural activities. Did you realise that the lettuce you buy today is deteriorating faster than you remember?
Before delving into the causes, effects and possible solutions for climate change mitigation and adaptation in the agricultural sector with the use of innovative technologies such as BIOAKSXTER® and ANTGRAN®, let's clarify what ‘climate change’ in agriculture really means, what its main causes and impacts are.
What is climate change in agriculture
Climate change in agriculture is a global phenomenon characterised by significant and sustained alterations in climatic parameters, such as temperature, precipitation and humidity, that directly affect agricultural activities. These variations lead to significant impacts on crops and food production, putting consumer safety and the sustainability of the agricultural sector at risk.
Examples are reduced yields and the very low nutritional value of agricultural products, or sudden frosts and heat waves that leave farmers and consumers facing a sudden shortage of fruit and vegetables.
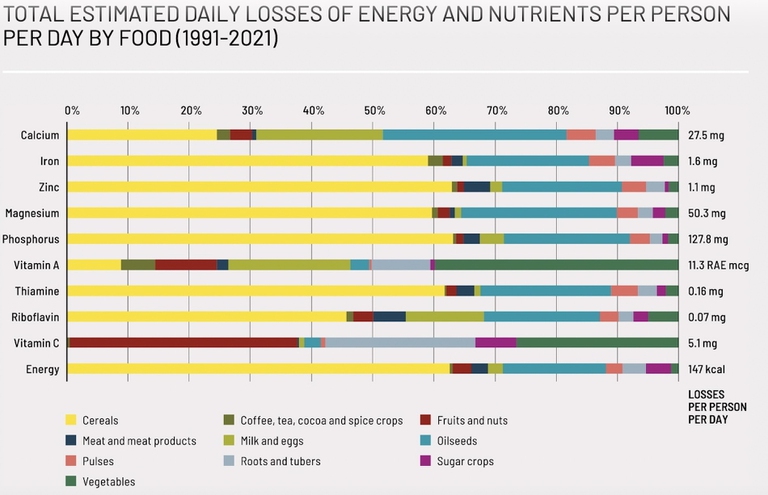
Loss of nutrients and energy from food per person per day from 1991 to 2021 linked to climate effects on agriculture © FAO
Causes of climate change in the agricultural sector
The main causes of climate change in the agricultural sector are directly linked to human actions: intensive farming practices, pollution and overexploitation of natural resources have altered and are destroying the climate balance.
The massive use of chemical fertilisers and plant protection products in general, while ‘boosting’ plant productivity, also contributes to the emission of polluting molecules into the environment and the release of greenhouse gases such as methane and nitrous oxide, exacerbating global warming. Do you sometimes think about what we are sacrificing for faster harvests?
Intensive livestock farming also has a devastating impact. Increased meat production requires huge amounts of natural resources and produces methane. Are we willing to ignore the fact that our eating habits are contributing to warming the planet?
In addition, there is the problem of deforestation to make room for new crops, a truly irreversible destruction of forests and woodlands, the main lungs of our planet.
Are we really balancing the needs of the present with those of future generations?
Impacts of climate change on agriculture and vice versa
How is climate change transforming agriculture? Climate change and agriculture are intrinsically linked in a complex cycle of cause and effect. On the one hand, climate change directly influences agricultural productivity, while on the other, agricultural practices contribute to climate change itself. We explore the most significant impacts of this interaction.
Changes in precipitation
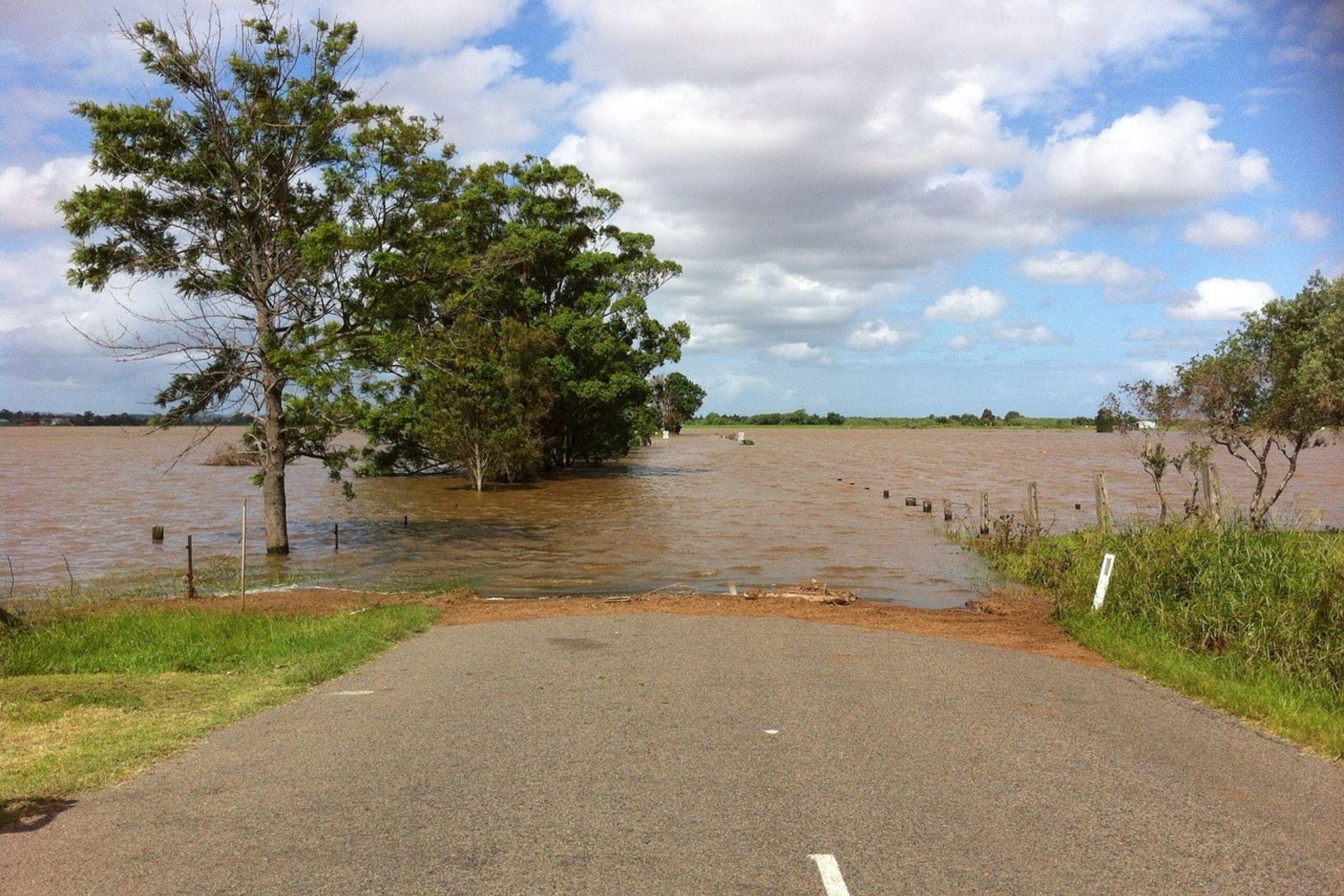
‘There are no more floods than there used to be’ is a phrase that many farmers frequently repeat today. Changes in rainfall patterns in agriculture are having major impacts worldwide, resulting in root asphyxia or droughts that have led to the loss of millions of hectares of arable land. The lack of regular and adequate rainfall leads to a water deficit that hampers crop growth, reducing yields and causing often irreparable damage.
Over the last 30 years, floods in Europe have become not only more frequent, but also more intense and prolonged than in the past. The seasonality of these climatic events has changed and, above all, the areas affected: Italy, the Czech Republic, Poland, Germany, Austria, Belgium and Romania are the countries most ‘battered’ by floods.

Rising temperatures
Did you know that exotic plants are now also grown in Italy? Shopping at the supermarket and reading the word ‘Italy’ on the labels of origin of tropical fruit is no longer an extraordinary thing.
The geography of crops is changing year after year and agriculture is forced to make constant changes. Farms are being called upon to replace plantations with new crops that are more suited to the area. An example of this is Sicily, which is currently uprooting citrus groves in several areas due to drought and desertification.
Rising temperatures have triggered stress phenomena in plants, impairing crop physiology and metabolism. Temperature stresses lead to reduced photosynthesis, excessive transpiration and increased susceptibility to diseases and pests. What will happen to agriculture if temperatures continue to rise?
Unavailability of agricultural land
One of the most serious problems related to the availability of agricultural land is soil pollution, which is undermining the productive capacity of large areas of the planet. Synthetic products used to increase productivity have actually poisoned soils. This means progressive loss of fertility and thus unproductive and increasingly less available arable land.
In many regions, soil contamination has reached levels that make cultivation impossible, forcing farmers to look for new areas to exploit, to the detriment of natural ecosystems.
Increase in plant diseases and spread of alien insects
Climate change favours the emergence and spread of plant diseases and contributes to the invasion of alien insects that further threaten agro-ecosystems worldwide.
With rising temperatures many pests and pathogens, previously confined to certain areas of the world, are colonising new territories. A concrete example is the spread of the Asian bug (Halyomorpha halys) in Europe, the olive fly (Bactrocera oleae) in Asia and Africa, and Xylella fastidiosa in Asia and Europe.
Climatic changes also provide favourable conditions for the development of fungal, bacterial and viral diseases, making crop management increasingly difficult.

What is the economic impact of climate change on the agricultural sector?
Climate change is dealing a severe blow to the global agricultural economy. Economic losses are evident not only at the level of individual crops, but also on a wider scale, involving the food chain and the world market. But how aware are we really of the price we are paying?
- Europe: overall, losses for the agricultural sector in the European Union are estimated at more than EUR 20 billion per year.
- Africa: estimated losses of around USD 50 billion per year.
- Asia: the Asian agricultural sector has suffered severe economic damage, with annual losses exceeding USD 70 billion.
- Latin America: growing challenges with estimated annual losses of USD 12 billion.
- North America: economic losses due to climate change in the agricultural sector are around USD 25 billion per year.
- Oceania: Climate change is reducing agricultural productivity with estimated annual losses of around USD 15 billion.
According to the Aon report, there were 398 natural disasters in 2023.
How climate change affects biodiversity
Climate change is having a number of direct and indirect negative impacts on the diversity of plant and animal species.
Firstly, changes in temperature and precipitation are altering natural habitats and affecting the geographical distribution of species. These changes result in geographic migrations of fauna and the inability of plants to adapt to the climate, leading to the dislocation of entire ecosystems. According to recent studies, extinction rates are also increasing due to climate change. Not to mention the reduction of genetic diversity within species.

How climate change affects consumer food safety
How does climate change affect the quality and availability of food that reaches our tables? Climate change is already causing alterations in the food supply chains, with consequences on:
- nutritional quality of food
- safety of agricultural products
- availability and prices of fruit and vegetables
Take for example cereals, one of the mainstays of global nutrition. The importance of cereals in global nutrition cannot be underestimated, just think of flour production or cattle feed, but droughts lead to reduced yields, triggering future concern about the availability of staple foods.
What about post-production spoilage? Climate change also affects food preservation, increasing waste throughout the supply chain (transport and storage).

Climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies in the agricultural sector
The agricultural sector can no longer afford to ignore the challenges imposed by climate change. However, there are innovative and sustainable strategies for mitigating the effects of climate on agriculture and adapting to these new conditions (Nature-Based Solutions NbS).
The most effective solutions are BioAksxter® depolluting fertiliser and AntGran® innovative hail protection and extreme weather event limiter.
Since pollution is the main cause of climate change in agriculture, it is essential to focus on BioAksxter®. Since the increase in hailstorms and storms are the consequence of climate change, it is essential to defend oneself with AntGran.
Despite recent developments in TEAs (Assisted Evolution Techniques) that aim to genetically modify crops to make them more resistant to climate change, it is important to be aware of their risks. Although promoted as quick fixes, TEAs have undesirable long-term effects on the ecosystem, risking irreversible alteration of biodiversity and compromising the natural evolution of species.
BioAksxter® and AntGran are distinguished by precisely the opposite approach. The one focuses on agriculture aimed at natural balances and soil regeneration without intervening at the genetic level, while the other puts the nightmare of hail out of mind.